Introduction
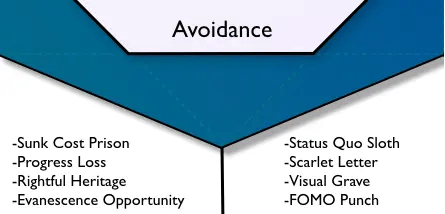
Image from https://yukaichou.com/gamification-examples/octalysis-complete-gamification-framework/
In the high-stakes environment of a chemical processing plant, where maintenance is crucial to operational efficiency and safety, the motivation of maintenance teams is paramount. Here, the ‘Loss & Avoidance’ core drive of the Octalysis Framework, a gamification strategy created by Yu-kai Chou, offers unique insights. This drive taps into the human desire to avoid adverse outcomes, which can strategically enhance maintenance procedures and execution.
Understanding ‘Loss & Avoidance’ in Maintenance
‘Loss & Avoidance’ is about the motivation to avoid negative consequences, such as loss of privileges, status, or the reversal of achievements, translating into strategies that encourage proactive behaviors to prevent equipment failure, safety incidents, or operational inefficiencies in maintenance.
Applying ‘Loss & Avoidance’ in Chemical Plant Maintenance
- Penalty for Missed Maintenance: Implement a system with clear consequences for missed or poorly executed maintenance tasks in the form of additional checks, reporting, or loss of certain privileges, emphasizing the importance of regular and thorough maintenance.
- Maintenance Streaks and Rewards: Encourage maintenance teams to maintain ‘streaks’ of successful, uninterrupted maintenance activities. Breaking the streak could result in losing certain rewards or recognition, motivating teams to adhere to schedules and procedures.
- Visualizing the Impact of Negligence: Use data and visual tools to demonstrate the potential negative consequences of maintenance negligence, such as equipment breakdowns or safety hazards. This tangible depiction can be a powerful motivator to maintain vigilance and protocol adherence.
- Scenario-Based Training: Conduct training that simulates scenarios where maintenance failures lead to adverse outcomes. This experiential learning can reinforce the importance of proper maintenance practices and avoiding loss.
- Accountability Measures: Establish clear accountability measures for maintenance tasks. Knowing that individual or team performance is closely monitored and linked to specific outcomes can encourage a more responsible approach to maintenance.
- Rewarding Proactive Maintenance: In contrast to penalties for negligence, reward proactive maintenance actions that prevent issues and losses. This positive reinforcement can balance the motivation derived from avoiding adverse outcomes.
- Safety and Efficiency Metrics: Tracking and reporting safety and efficiency metrics regularly to maintain high standards and avoid declining these metrics can drive continuous improvement in maintenance practices.
- Loss Aversion in Resource Management: Implementing resource management strategies highlighting the cost of wasted resources due to poor maintenance, such as energy loss or increased wear and tear on equipment, motivates teams to optimize maintenance activities to avoid such losses.
Conclusion
By integrating the ‘Loss & Avoidance’ drive from the Octalysis Framework into the maintenance strategy of a chemical processing plant, you can significantly enhance the attentiveness and diligence of maintenance teams. This approach leverages a fundamental aspect of human behavior to ensure that maintenance activities are carried out efficiently, safely, and consistently. While balancing this drive with positive reinforcement strategies is crucial, ‘Loss and avoidance’ can be a powerful tool in maintaining high standards and preventing complacency in critical maintenance operations.
To learn directly from Yu-Kai’s site:
The information in this article was partially generated by OpenAI’s ChatGPT, an AI language model, and has been reviewed/edited for accuracy and relevance. OpenAI. (2024). ChatGPT [Large language model]. Retrieved from https://chat.openai.com/




Leave a comment