Image from https://yukaichou.com/gamification-examples/octalysis-complete-gamification-framework/
Introduction:
In the intricate ecosystem of a chemical processing plant, motivating employees to engage actively with Environmental Management Systems (EMS) can be challenging. The Octalysis framework, crafted by Yu-kai Chou, introduces an intriguing “Loss & Avoidance” aspect that can be strategically applied to EMS. This blog post examines how the “Loss & Avoidance” core drive can be leveraged to bolster environmental practices, fostering a more responsible and proactive approach to environmental management in the industry.
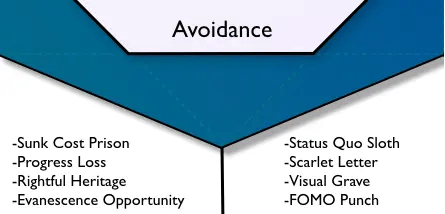
Understanding Loss & Avoidance:
The “Loss & Avoidance” core drive is based on the human tendency to avoid adverse outcomes or losses. In a workplace setting, this can translate into mechanisms that encourage employees to engage in positive environmental behaviors to avoid negative consequences, both real and perceived.
Application in Environmental Management:
- Environmental Compliance Scorecards: Implement a scorecard system that tracks each department’s adherence to environmental standards. The prospect of receiving a low score or publicizing underperformance can motivate teams to avoid this negative outcome.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Establish clear penalties for failing to adhere to environmental policies. This could range from formal warnings to impact on performance reviews. The aim is to create a tangible consequence for not meeting environmental standards.
- Loss Aversion Incentives: Create incentives where employees start with certain privileges or benefits that can be lost if environmental targets are unmet. For example, additional break time or a preferred parking spot could be at stake, leveraging the desire to maintain these benefits.
- Environmental Risk Simulations: Conduct simulations or training sessions that showcase the potential risks and negative impacts of poor environmental management. Employees are more likely to adhere to best practices by visualizing the consequences of negligence.
- Sustainability-linked Performance Metrics: Integrate environmental performance metrics into individual performance reviews. The possibility of a negative review due to poor environmental practices can drive employees to avoid this outcome by being more conscientious.
Benefits and Impact:
- Increased Compliance and Awareness: Using loss and avoidance strategies can lead to heightened compliance with environmental policies and greater awareness of the importance of EMS.
- Proactive Environmental Stewardship: Employees are likely to take a more proactive role in environmental management to avoid adverse outcomes.
- Cultural Shift Towards Responsibility: Over time, these practices can contribute to a cultural shift where environmental responsibility becomes a fundamental part of the organization’s ethos.
- Tangible Improvements in EMS: The fear of loss or negative consequences can result in tangible improvements in environmental performance and sustainability initiatives.
Conclusion:
Incorporating the “Loss & Avoidance” core drive from the Octalysis framework into EMS strategies at chemical processing plants can significantly enhance the effectiveness of these systems. By leveraging the natural human tendency to avoid loss and negative outcomes, plants can motivate employees to engage more deeply with environmental responsibilities. This approach ensures compliance with environmental standards and fosters a culture of proactive and responsible environmental stewardship, crucial for the sustainability of the industry and the planet.
To learn directly from Yu-Kai’s site:
The information in this article was partially generated by OpenAI’s ChatGPT, an AI language model, and has been reviewed/edited for accuracy and relevance. OpenAI. (2024). ChatGPT [Large language model]. Retrieved from https://chat.openai.com/



Leave a comment